What does the grit size indicate?
Macrogrits: 16, 20, 24, 30, 36, 40, 50, 60, 80, 100, 120, 150, 180, 220.
Microgrits: 240, 280, 320, 360, 400, 500, 600, 800, 1000, 1200, 1500, 2000


Grit numbering
To ensure international standards for abrasive grit size, there are different international organisations:
ANSI: American National Standards Institute.
CAMI: Coated Abrasives Manufacturers Institute.
FEPA: Federation of European Producers of Abrasives.
JIS: Japanese Standards Association
In Europe, grit sizes, measurements and naming are regulated by the FEPA regulations. It is an association of European manufacturers of abrasive products that includes members from the world's largest manufacturers for the different industrial sectors: automotive, aerospace, electronics, building and construction, metal production, engineering, services, DIY, etc.
Depending on the type of abrasive, the grit sizes are preceded by different letters:
Letter F for bonded or adhered abrasives.
Letter P for coated or covered abrasives and non-woven abrasives.
Letters D and B for diamond and boron nitride superabrasives respectively.
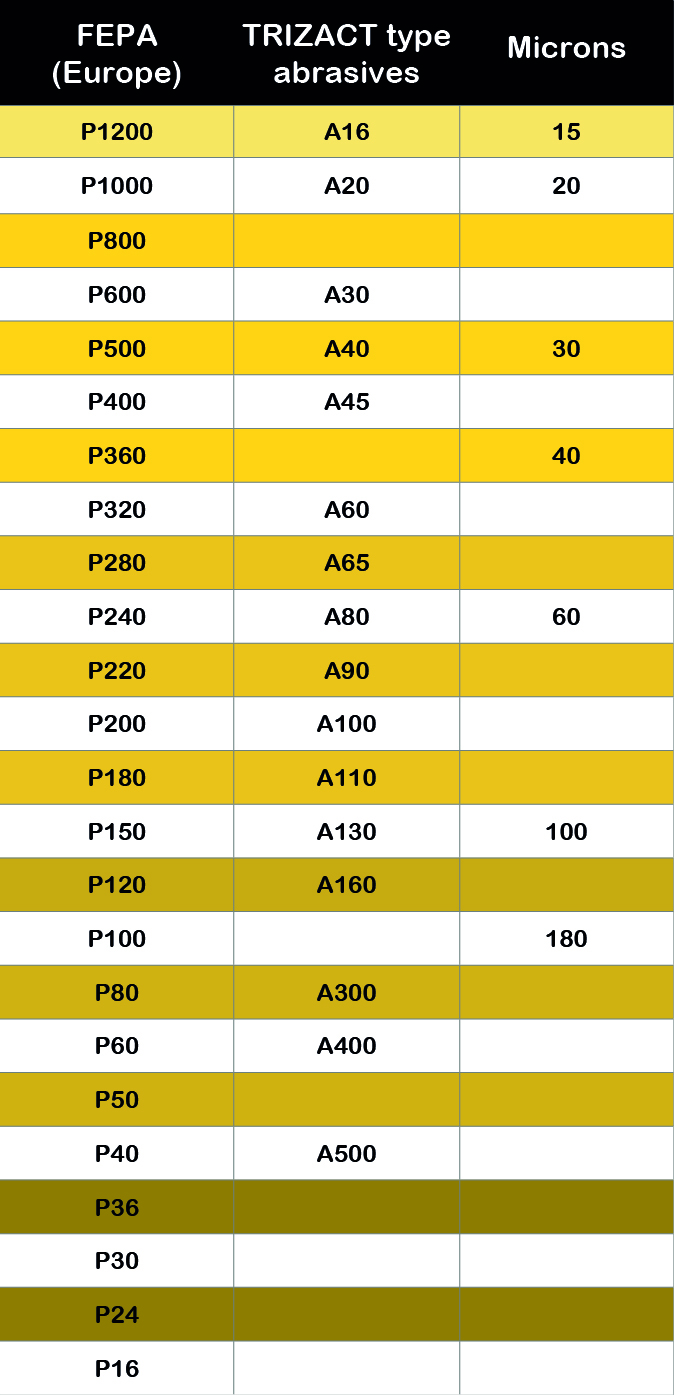
In addition to these nomenclatures, there are other designations, the best known of which are Trizact for structured grits and the designation Micron for film products for finishing and microfinishing.
Scaling of abrasive grains
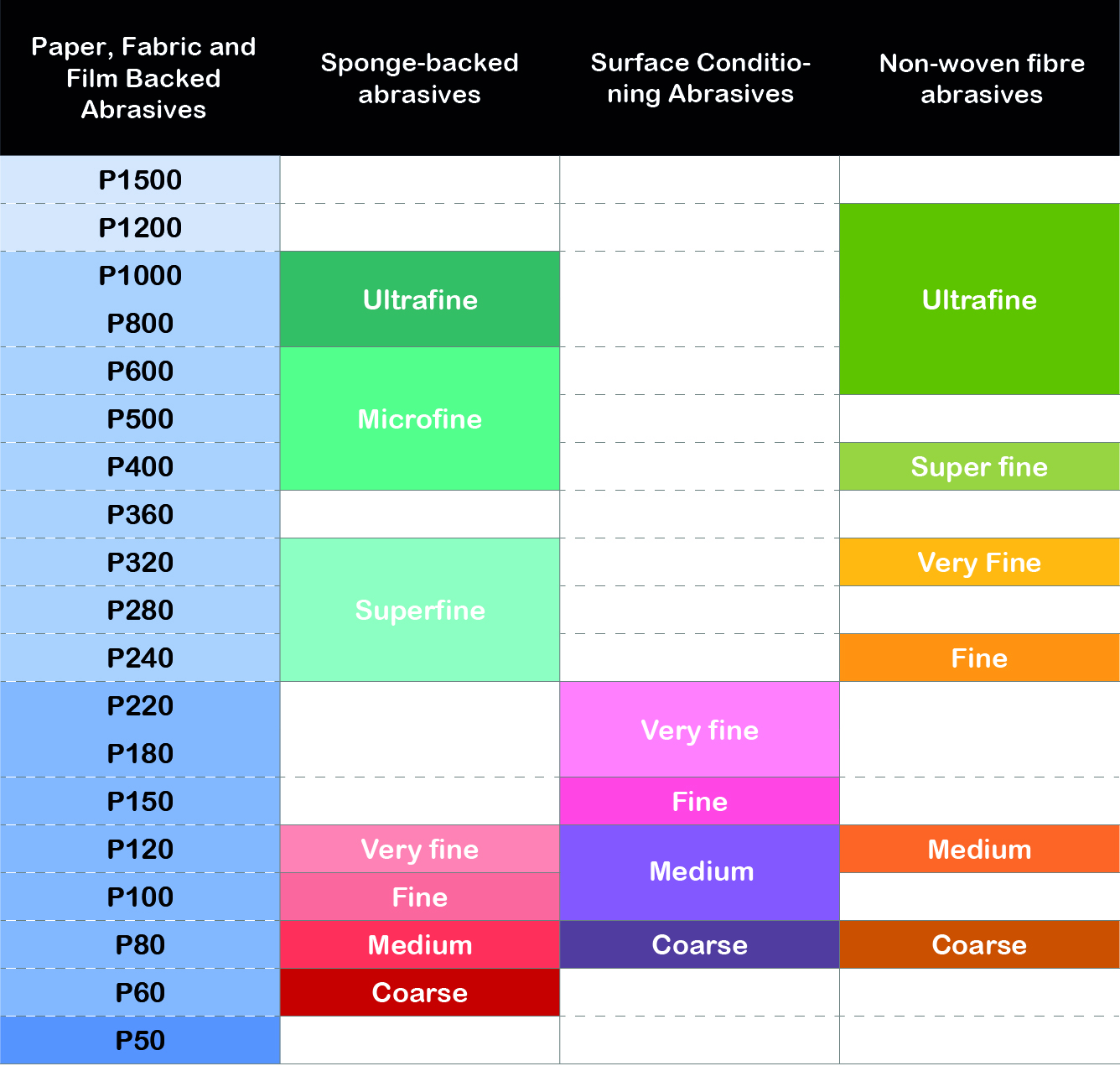
Equivalences according to grit
Knowing the equivalences between the different types of coated abrasives and their finishing grades will help us to carry out successful sanding processes, being able to alternate different types and formats of abrasives, without damaging the work done in the previous steps.
The following table provides an approximate equivalence between the most common abrasives depending on the type of support. The finish of surface conditioning abrasives and non-woven fibre abrasives will be more satin compared to the appearance of a surface treated with traditional abrasive products with paper, cloth, combination or film supports.